In This Article
Coenzyme Q is an antioxidant naturally made in human body. All cells in your body have CoQ because they need it for basic functions. Your body produces this coenzyme, and the function of coenzyme is to produce energy that is much needed for cell growth and maintenance. This potent antioxidant is thought to be extremely beneficial for your health as it protects your body from diseases and conditions associated with aging. In this article, we’re going to discuss the role of coenzyme Q in dietary therapy against aging. Let’s see how it can help you.
All you have to do is keep reading and discover more information on Coenzyme Q and the role of coq10 in the body. As you will be able to see, coq10 for anti aging is an actual thing – you can use it to defeat the stand of time and look more amazing than ever. The coenzyme q10 anti aging benefits are plenty, starting with the fact that the general appearance of the skin is immediately improved. When it comes to q10 anti aging treatments, you have to keep in mind that this enzyme is one of the most efficient weapons against the aging process.
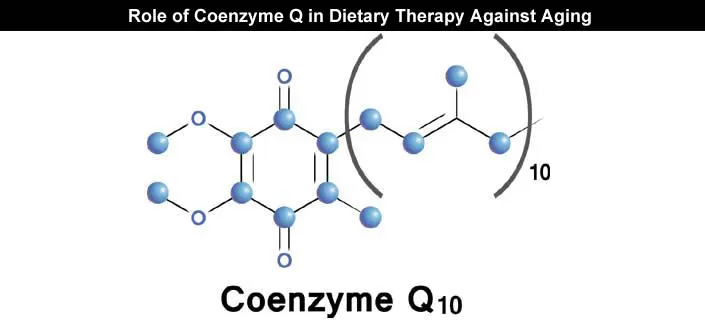
Physiological Roles of Coenzyme Q
Coenzyme Q was isolated and defined in 1955 and just two years later it proved to be a crucial mitochondrial electron transport chain component. [1]
As mentioned already, it is an important factor for cell bioenergetics and one of its main functions in your body is the role of an antioxidant. CoQ constitutes the only lipid-soluble antioxidant endogenously synthesized that is proved to successfully prevent oxidation of lipids, DNA, and proteins. Moreover, it also takes part in regeneration of other antioxidants such as ascorbate or Vitamin C.
According to review of studies published in Molecules and conducted by Alfonso Varela-Lopez and team of scientists of the University of Granada in Spain, multiple scientific works have revealed that coenzyme Q offers protection against apoptosis (cell death) by inducing the inhibition of cell death independently from free radical destroying properties and antioxidant effects. [2]
Levels of CoQ(Coenzyme Q) and Aging
Same review of studies we’ve mentioned above states that levels of CoQ start decreasing as we age and this reduction depends on tissues, organisms and many other factors. [3]
This explains why some studies discovered reduction of CoQ in initial phases of aging while others spotted decrease in advanced stages of aging process. [4]
Lower levels of coenzyme Q are associated with several age-related pathologies. For example, cardiovascular diseases, neuropathies, metabolic syndrome, inflammation, arthritis, carcinogenesis, hypercholesterolemia, and diabetes aggravate in advanced stages of life and risk for suffering from these pathologies increases with your age. Several studies revealed that coenzyme Q has beneficial effect on these diseases. [5]
Furthermore, scientific studies associated lower levels of CoQ with some neurodegenerative diseases as well. For example, one study found lower levels of this coenzyme in cerebrospinal fluid of patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease.
Low levels of CoQ are linked with development of several types of cancer such as melanoma, breast cancer, myeloma, Graves’ disease etc. With that being said, various studies have also discovered that tumorous cells have significantly lower levels of coenzyme Q than healthy cells.
Dietary Therapies and Coenzyme Q
According to data from multiple studies, dietary supplementation with this coenzyme could prove to be an effective anti-aging tactic. There’s a growing number of evidence that intake of CoQ10 can result in its successful incorporation into mitochondria. There, the coenzyme enhances transfer of electrons and improves various pathologies such as cardiac failure, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, and Friedreich’s ataxia (inherited disease that causes progressive damage to the nervous system).
Several studies have been conducted to inspect the role of coenzyme Q10 supplementation and lifespan. Here are key points:
- Effects of long-term supplementation with CoQ10 significantly increased mean and maximum lifespan in rats fed diet rich in n-6 PUFA(polyunsarturated fatty acids)
- When sunflower oil was the main fat in the diet, coenzyme Q supplementation improved endocrine pancreas structure and had similar effects as olive oil
- CoQ (Coenzyme Q) enhances cellular antioxidant protection systems in cell membranes
- CoQ prevents lipid peroxidation,
- Supplementation with CoQ is associated with lower impairment of coq10 mitochondrial function.
All these results suggest that coenzyme Q supplementation prevents lifespan shortening because of oxidative insults. Scientists who conducted a review of studies we discussed in this article pointed out it’s very difficult to determine the ideal conditions for usage of coenzyme Q as anti-aging therapy. It’s because studies reviewed in this research included different dosages, chemical formulations, subjects of different ages etc. Experts stress the importance of further studies on this coenzyme in order to inspect all its benefits and roles in relieving various pathologies linked with aging. To slow down your aging you may peep on anti aging reviews such as Dermapen Review here.
Sources of Coenzyme Q
It was already mentioned that our body makes this enzyme naturally, but it’s also possible to find it in food. Approximately 6% of orally administered CoQ spreads through the gastrointestinal tract into the blood and then it’s transferred to spleen and liver.
Table: Some Food Sources of Coenzyme Q
| Food | Serving | Coenzyme Q10 (mg) |
| Beef, fried | 3 ounces* | 2.6 |
| Herring, marinated | 3 ounces | 2.3 |
| Chicken, fried | 3 ounces | 1.4 |
| Soybean oil | 1 tablespoon | 1.3 |
| Canola oil | 1 tablespoon | 1.0 |
| Rainbow trout, steamed | 3 ounces | 0.9 |
| Peanuts, roasted | 1 ounce | 0.8 |
| Sesame seeds, roasted | 1 ounce | 0.7 |
| Pistachio nuts, roasted | 1 ounce | 0.6 |
| Broccoli, boiled | ½ cup, chopped | 0.5 |
| Cauliflower, boiled | ½ cup, chopped | 0.4 |
| Orange | 1 medium | 0.3 |
| Strawberries | ½ cup | 0.1 |
| Egg, boiled | 1 medium | 0.1 |
*A 3-ounce serving of meat or fish is about the size of a deck of cards.
According to University of Maryland main dietary sources of CoQ include organ meats (e.g. heart, liver and kidneys), oily fish (e.g. salmon) and whole grains.
Other sources of coenzyme Q include:
- Eggs
- Spinach
- Broccoli
- Peanuts
Although most people get sufficient amount of coenzyme Q through well-balanced diet, there’s still option to take supplements. However, before you opt to use supplements you should consult your doctor, particularly if you’re already taking medications for some chronic condition or disease.
What is coenzyme q?
Coenzyme q is an important antioxidant produced within the human body. Naturally-produced, it is used by different cells in the body in order to maintain their cellular functions. It is a common fact that the levels of coenzyme q decrease with age, which in turn can affect different organs and systems.
What does coenzyme q do?
Coenzyme q is essential for many different cellular functions. As it is an antioxidant, it protects the different organs and systems of the body against the damage done by free radicals. It also plays a role in the cellular energy production and cell metabolism. It plays an essential role in maintaining the cells in a young state, for as long as it is possible.
What does coenzyme q10 do?
As already mentioned, the role of coq10 is to maintain a proper state of functioning in various cells. The function of coenzyme q10 has been studied for a long period of time, and it was recently determined that the enzyme acts as an antioxidant, thus protecting the body against oxidative stress.
Why coenzyme q for aging?
Antioxidants can offer enhanced protection against the physiological aging process. Coenzyme q is one of the most efficient weapons in the anti-aging battle, being a potent antioxidant – it can repair the damage done by free radicals and provide the necessary protection against further damage. Moreover, it works to improve the general appearance of the skin and make common signs of aging, such as fine lines and wrinkles, less visible. You can dig deep on top rated anti aging reviews which contain antioxidant on our sites.
Final Verdict
Coenzyme Q is naturally produced in our bodies where it performs highly important roles as an antioxidant. It comes as no wonder that various ailments associated with advanced age are linked with lower levels of CoQ. Although dietary therapy with coenzyme Q is beneficial for overall health and prevention of age-related pathologies, identifying the ideal conditions can be rather difficult. Instead of doing it on your own you should consult your doctor which you should also do before you buy supplements.
As you have seen, Coenzyme Q can help you look young all over again. When it comes to coq10 for anti aging, you need to remember its antioxidant properties and its effects at the level of the skin. Numerous studies have confirmed the role of coenzyme q10 and its anti aging properties, especially when used on a regular basis.
5 Sources
We review published medical research in respected scientific journals to arrive at our conclusions about a product or health topic. This ensures the highest standard of scientific accuracy.
[1] Coenzyme Q and Its Role in the Dietary Therapy against Aging: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030373[2] Varela-López A, Giampieri F, Battino M, Quiles JL. Coenzyme Q and Its Role in the Dietary Therapy against Aging. Molecules. 2016;21(3):373. Published 2016 Mar 18. doi:10.3390/molecules21030373
[3] Hernández-Camacho JD, Bernier M, López-Lluch G, Navas P. Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation in Aging and Disease. Front Physiol. 2018;9:44. Published 2018 Feb 5. doi:10.3389/fphys.2018.00044
[4] Barcelos IP, Haas RH. CoQ10 and Aging. Biology (Basel). 2019;8(2):28. Published 2019 May 11. doi:10.3390/biology8020028
[5] Cirilli I, Damiani E, Dludla PV, et al. Role of Coenzyme Q10 in Health and Disease: An Update on the Last 10 Years (2010-2020). Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(8):1325. Published 2021 Aug 23. doi:10.3390/antiox10081325









 This article changed my life!
This article changed my life! This article was informative.
This article was informative. I have a medical question.
I have a medical question.
 This article contains incorrect information.
This article contains incorrect information. This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.
This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.