Lumpy, uneven skin on the thighs, buttocks, and abdomen – that’s cellulite, a common concern for many, especially women. It’s not a health risk, but it can affect self-confidence and lead to a desire for smoother, more toned skin. While maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly are crucial for overall cellulite management, new technologies like Ultrasound Cavitation (UC) offer a promising non-invasive approach. [1]
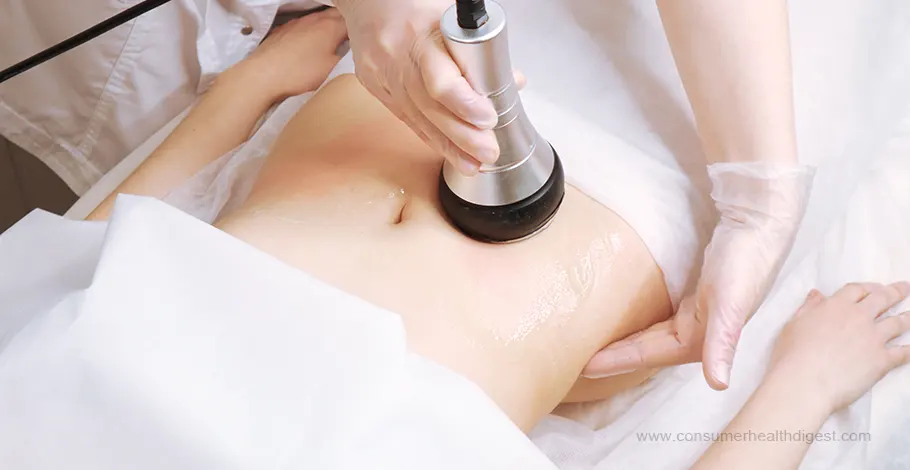
What is Ultrasound Cavitation?
According to the National Institute of Health, Ultrasound Cavitation utilizes low-frequency sound waves to target fat cells beneath the skin’s surface. Imagine tiny vibrations shaking things up! These sound waves gently disrupt the fat cell membranes, causing them to rupture and release their stored fat. The body then takes over, naturally processing and eliminating the broken-down fat through the lymphatic system and urine. [2]
How Does Ultrasonic Cavitation (UCRF) Work?
Utilizing an ultrasound machine, the practitioner employs gentle strokes and circular motions over the cellulite-affected area of the body. An anti-inflammatory gel or cream may accompany the procedure for enhanced efficacy.
The machine emits high-frequency sound waves, precisely targeting cellulite and inducing tissue vibrations. This deep penetration stimulates blood flow to the region, triggering immediate tissue recovery and fat release. Typically, the process lasts just a few minutes and is entirely painless.
Additionally, women may opt for slim plastering as a complementary treatment. This method aims to enhance skin appearance and reduce cellulite or stretch marks. During the session, the affected area is covered with plaster.
After four hours, individuals resume their daily activities before returning to the clinic for plaster removal. The plaster contains ingredients such as horse chestnut, gotu kola extract, algae, and pineapple enzymes, promoting cellulite removal.
Benefits of Ultrasound Cavitation for Cellulite
UC offers several potential benefits in the fight against cellulite:
- Reduced Cellulite Appearance: Studies have shown promising results for UC in reducing the appearance of cellulite. The targeted breakdown of fat cells in specific areas, like thighs or abdomen, can lead to a smoother, less dimpled appearance. [3]
- Targeted Fat Reduction: UC allows for a more targeted approach, unlike traditional weight loss methods. It can address stubborn fat deposits that may not respond well to diet and exercise alone.
- Improved Skin Texture and Elasticity: While UC primarily targets fat cells, it may also have a positive impact on skin texture and elasticity. This is because the treatment process can stimulate collagen production, a protein that provides structure and firmness to the skin. Smoother, tighter skin can further enhance the reduction in cellulite visibility. [4]
- Non-invasive Treatment: Unlike liposuction, UC is a non-invasive procedure. It doesn’t involve needles, scalpels, or downtime. Treatments are typically performed in a comfortable spa-like setting.
Important Considerations for UC Treatment
While UC offers a promising approach, some important factors to consider before undergoing treatment include:
- Number of Sessions: For optimal results, multiple UC sessions are typically recommended. The specific number will depend on the severity of cellulite and the desired outcome.
- Consultation with a Healthcare Professional: Consulting a doctor or licensed aesthetician is crucial before starting UC treatment. They can assess your suitability, discuss potential risks and benefits, and create a personalized treatment plan.
- Potential Side Effects: UC is generally considered safe, but some temporary side effects may occur, like mild redness, bruising, or tenderness in the treated area. These side effects typically resolve within a few days.
Beyond UC: A Holistic Approach to Cellulite Reduction
While UC can be a valuable tool, it’s important to remember that it’s not a magic bullet. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle remains the cornerstone of effective cellulite management. Here are some additional strategies to consider [5]:
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains gives your body the nutrients it needs to function optimally. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can also contribute to cellulite reduction.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, especially exercises that target the legs and glutes, helps build muscle and improve circulation. This can improve the appearance of cellulite and promote overall fitness.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: While UC can target specific fat deposits, it’s not intended for overall weight loss. Being at a healthy weight can significantly reduce the appearance of cellulite.
Conclusion
Cellulite is a common concern, and achieving smoother, more toned skin might require a multi-pronged approach. Ultrasound Cavitation offers a promising non-invasive technique to target stubborn fat deposits and potentially reduce the appearance of cellulite. However, it’s important to maintain realistic expectations and consider it a tool alongside a healthy lifestyle.
If you’re interested in learning more about UC and its suitability for you, consult a healthcare professional who can discuss your individual needs and goals. Remember, with a combination of UC, a healthy lifestyle, and a positive outlook, you can be well on your way to achieving smoother, more confident skin.
5 Sources
We review published medical research in respected scientific journals to arrive at our conclusions about a product or health topic. This ensures the highest standard of scientific accuracy.
[2] da Silva RMV, Santos JC, de Carvalho WLM, de Vasconcellos LS, de Castro ABF, Borges FDS, Carreiro EM, Meyer PF. Effects of Ultracavitation and Radiofrequency on Abdominal Adiposity. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022 Jan;15(1):E66-E71. PMID: 35309273; PMCID: PMC8903231.
[3] Gabriel A, Chan V, Caldarella M, Wayne T, O'Rorke E. Cellulite: Current Understanding and Treatment. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2023 Jun 21;5:ojad050. doi: 10.1093/asjof/ojad050. PMID: 37424836; PMCID: PMC10324940.
[4] Bani D, Quattrini Li A, Freschi G, Russo GL. Histological and Ultrastructural Effects of Ultrasound-induced Cavitation on Human Skin Adipose Tissue. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2013 Oct 7;1(6):e41. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0b013e3182a7f222. PMID: 25289235; PMCID: PMC4174158.
[5] Friedmann DP, Vick GL, Mishra V. Cellulite: a review with a focus on subcision. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017 Jan 7;10:17-23. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S95830. PMID: 28123311; PMCID: PMC5234561.






 This article changed my life!
This article changed my life! This article was informative.
This article was informative. I have a medical question.
I have a medical question.
 This article contains incorrect information.
This article contains incorrect information. This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.
This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.